Adverse reactions in HER2CLIMB
Of the most common adverse reactions in the TUKYSA arm, a majority were Grade 1 or 21
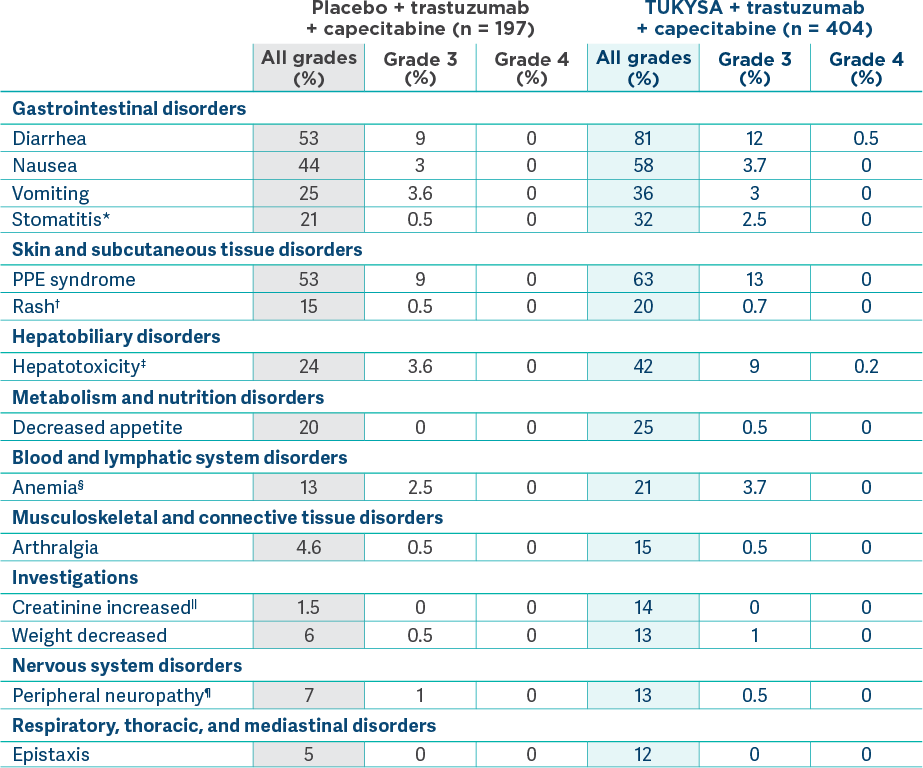
Adverse reactions (≥10%) in patients who received TUKYSA and with a difference between arms of ≥5% compared to placebo in HER2CLIMB2
Serious adverse reactions occurring in ≥2% of patients in the TUKYSA
- Any reaction: 26% (diarrhea, 4.0%; vomiting, 2.5%; nausea, 2.0%; abdominal pain,
2.0%; seizure,
2.0%)2 - Fatal reactions: 2%, including sudden death, sepsis, dehydration, and cardiogenic
shock1,2 - Laboratory abnormalities (≥20%) worsening from baseline in patients who received TUKYSA and with a
difference of ≥5% compared to placebo in HER2CLIMB were decreased hemoglobin (59% vs 51% [Grade ≥3,
3.3% vs 1.5%]), decreased phosphate (57% vs 45%), increased bilirubin (47% vs 30%), increased ALT
(46% vs 27%), increased AST (43% vs 25%), decreased magnesium (40% vs 25%), decreased potassium (36%
vs 31%), increased creatinine (33% vs 6%), decreased sodium (28% vs 23%), and increased alkaline
phosphatase (26% vs 1
7%)2
*Stomatitis includes stomatitis, oropharyngeal pain, oropharyngeal
discomfort, mouth ulceration, oral pain, lip ulceration, glossodynia, tongue blistering, lip
blister, oral dysesthesia, tongue ulceration, and aphthous
†Rash includes rash maculo-papular, rash, dermatitis acneiform, erythema, rash macular,
rash papular, rash pustular, rash pruritic, rash erythematous, skin exfoliation, urticaria,
dermatitis allergic, palmar erythema, plantar erythema, skin toxicity, and
‡Hepatotoxicity includes hyperbilirubinemia, blood bilirubin increased, bilirubin
conjugated increased, alanine aminotransferase increased, transaminases increased, hepatotoxicity,
aspartate aminotransferase increased, liver function test increased, liver injury, and
hepatocellular
§Anemia includes anemia, hemoglobin decreased, and normocytic
||Due to inhibition of renal tubular transport of creatinine without affecting glomerular
¶Peripheral neuropathy includes peripheral sensory neuropathy, neuropathy peripheral,
peripheral motor neuropathy, and peripheral sensorimotor
#An adverse reaction is considered serious if it results in death, is life-threatening,
requires inpatient hospitalization or prolongation of existing hospitalization, results in
disability, or causes a congenital anomaly/birth
ALT = alanine aminotransferase; AST = aspartate aminotransferase; PPE = palmar-plantar
erythrodysesthesia.
Adverse reactions of clinical interest
The Prescribing Information for TUKYSA contains warnings and precautions for diarrhea, hepatotoxicity, and embryo-fetal toxicity, some of which may be severe or fatal. Please see full Important Safety Information for more
Diarrhea
- Antidiarrheal prophylaxis was not required in the HER2CLIMB trial
protocol4
- TUKYSA can cause severe diarrhea including dehydration, hypotension, acute kidney injury, and
death2
- Median time to onset (any grade) was 12
days2 - Median time to resolution was 8
days2 - Median duration of antidiarrheal use was 3 days for each 21-day repeating
regimen1
- Diarrhea led to TUKYSA dose reductions in 6% of patients and TUKYSA permanent discontinuation in
1% of
patients2 - If diarrhea occurs, administer antidiarrheal treatment and perform diagnostic tests to exclude
other causes, as clinically indicated; based on the severity, interrupt dose and then dose
reduce or permanently discontinue
TUKYSA2 - 81% of patients who received TUKYSA experienced diarrhea, including 0.5% with Grade 4 and 12%
with Grade 3. Both patients who developed Grade 4 diarrhea subsequently died, with diarrhea as a
contributor to
death2
Hepatotoxicity
- TUKYSA can cause severe
hepatotoxicity2
- 8% of patients who received TUKYSA had an ALT increase >5 x ULN, 6% had an AST increase >5
x ULN, and 1.5% had a bilirubin increase >3 x ULN (Grade
≥3)2
- Hepatotoxicity led to TUKYSA dose reductions in 8% of patients and TUKYSA permanent
discontinuation in 1.5% of
patients2 - Monitor ALT, AST, and bilirubin prior to starting TUKYSA, every 3 weeks during treatment, and as
clinically indicated. Based on the severity of hepatotoxicity, interrupt dose, then dose reduce
or permanently
discontinue2
Interstitial lung disease
- There was 1 case of ILD in HER2CLIMB (Grade 1 pneumonitis in the TUKYSA arm), which was not
considered by the investigator to be caused by the study’s
agents5
Alopecia
- Alopecia was infrequent and mostly Grade 1 (all grades: 4.7% in the TUKYSA arm, 3.6% in the
control arm; there was 1 case of Grade 2 alopecia in each
arm)5,6
For information on how to manage select adverse reactions associated with TUKYSA, trastuzumab, and capecitabine, please refer to the respective Prescribing Information for each agent.
ILD = interstitial lung disease; ULN = upper limit of normal.
Dose adjustments in HER2CLIMB
Frequencies of modifications and discontinuations are descriptive data that are not intended to
provide conclusions about safety and should be interpreted with caution.
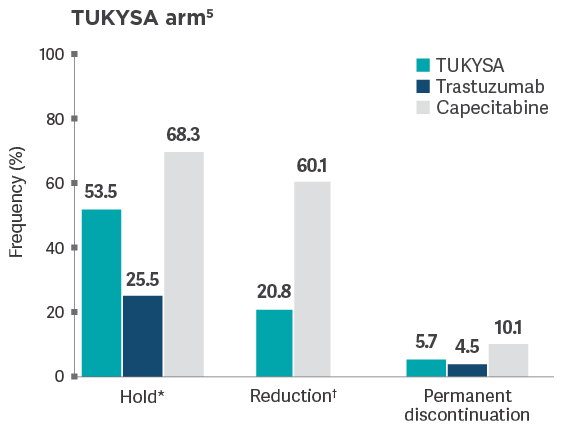
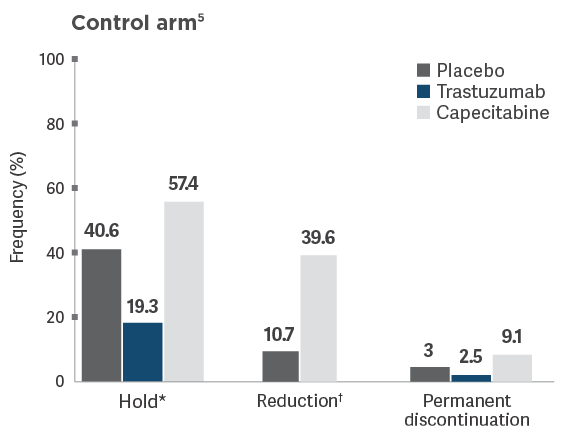
Permanent
discontinuation rates due to adverse
Tukysa
6%
vs
Placebo
3%
- Adverse reactions leading to permanent discontinuation of TUKYSA in ≥1% of patients were hepatotoxicity (1.5%) and diarrhea (1%)2
- Adverse reactions leading to dose reduction of TUKYSA in ≥2% of patients were hepatotoxicity (8%) and diarrhea (6%)2
*Dose hold frequency for trastuzumab included interruptions during infusion of trastuzumab.5
†Reduction of the trastuzumab dose was not allowed per HER2CLIMB protocol.5
Safety profile at 2-year follow-up7
Follow-up safety analysis was conducted as part of a prespecified exploratory analysis. Results are presented as descriptive data that are not intended to provide conclusions about safety and should be interpreted with caution. Data cutoff for follow-up analysis was February 8, 2021.
TEAEs Grade ≥3*
61% (n = 245/404) in the TUKYSA arm vs 51% (n = 101/197) in the control arm
TEAEs leading to death*
2% (n = 6/404) in the TUKYSA arm vs 3% (n = 5/197) in the control arm
The permanent discontinuation rate at the follow-up analysis for the TUKYSA arm remained consistent with
the primary analysis7
Permanent discontinuation rates due to TEAEs*
Tukysa
6%
vs
Placebo
4%
- Permanent discontinuation rates of capecitabine due to TEAEs were 12% in the TUKYSA arm and 11% in the control arm
- Permanent discontinuation rates of trastuzumab due to TEAEs were 4% in the TUKYSA arm and 4% in the control arm
- Dose hold and dose reduction data were not captured for this analysis
77% of patients in the TUKYSA arm received subsequent anticancer treatment7
Results are descriptive but not conclusive, are not controlled for type 1 error, and should be interpreted with caution.
*TEAEs are events that are new or worsened on or after receiving the first dose of treatment and through 30 days after the last dose of treatment.7
TEAE = treatment-emergent adverse event.
Important Safety Information
Warnings and Precautions
-
Diarrhea: TUKYSA can cause severe diarrhea including
dehydration, hypotension, acute kidney injury, and death. If diarrhea
occurs, administer antidiarrheal treatment as clinically indicated.
Perform diagnostic tests as clinically indicated to exclude other
causes of diarrhea. Based on the severity of the diarrhea, interrupt
dose, then dose reduce or permanently discontinue TUKYSA.
In HER2CLIMB, when TUKYSA was given in combination with trastuzumab and capecitabine, 81% of patients who received TUKYSA experienced diarrhea, including 0.5% with Grade 4 and 12% with Grade 3. Both patients who developed Grade 4 diarrhea subsequently died, with diarrhea as a contributor to death. Median time to onset of the first episode of diarrhea was 12 days and the median time to resolution was 8 days. Diarrhea led to TUKYSA dose reductions in 6% of patients and TUKYSA discontinuation in 1% of patients. Prophylactic use of antidiarrheal treatment was not required on HER2CLIMB. -
Hepatotoxicity: TUKYSA can cause severe
hepatotoxicity. Monitor ALT, AST, and bilirubin prior to starting
TUKYSA, every 3 weeks during treatment, and as clinically indicated.
Based on the severity of hepatotoxicity, interrupt dose, then dose
reduce or permanently discontinue TUKYSA.
In HER2CLIMB, 8% of patients who received TUKYSA had an ALT increase >5 × ULN, 6% had an AST increase >5 × ULN, and 1.5% had a bilirubin increase >3 × ULN (Grade ≥3). Hepatotoxicity led to TUKYSA dose reductions in 8% of patients and TUKYSA discontinuation in 1.5% of patients. - Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: TUKYSA can cause fetal harm. Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential, and male patients with female partners of reproductive potential, to use effective contraception during TUKYSA treatment and for 1 week after the last dose.
Adverse Reactions
In HER2CLIMB, serious adverse reactions occurred in 26% of patients
who received TUKYSA; the most common (in ≥2% of patients) were
diarrhea (4%), vomiting (2.5%), nausea (2%), abdominal pain (2%), and
seizure (2%). Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 2% of patients who
received TUKYSA including sudden death, sepsis, dehydration, and
cardiogenic shock.
Adverse reactions led to treatment discontinuation in 6% of patients
who received TUKYSA; the most common (in ≥1% of patients) were
hepatotoxicity (1.5%) and diarrhea (1%). Adverse reactions led to dose
reduction in 21% of patients who received TUKYSA; the most common (in
≥2% of patients) were hepatotoxicity (8%) and diarrhea (6%).
The most common adverse reactions in patients who received TUKYSA
(≥20%) were diarrhea, palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia, nausea,
hepatotoxicity, vomiting, stomatitis, decreased appetite, anemia, and
rash.
Lab Abnormalities
In HER2CLIMB, Grade ≥3 laboratory abnormalities reported in ≥5% of patients who received TUKYSA were decreased phosphate, increased ALT, decreased potassium, and increased AST.
The mean increase in serum creatinine was 32% within the first 21 days of treatment with TUKYSA. The serum creatinine increases persisted throughout treatment and were reversible upon treatment completion. Consider alternative markers of renal function if persistent elevations in serum creatinine are observed.
Drug Interactions
- Strong CYP3A/Moderate CYP2C8 Inducers: Concomitant use may decrease TUKYSA activity. Avoid concomitant use of TUKYSA.
- Strong or Moderate CYP2C8 Inhibitors: Concomitant use of TUKYSA with a strong CYP2C8 inhibitor may increase the risk of TUKYSA toxicity; avoid concomitant use. Increase monitoring for TUKYSA toxicity with moderate CYP2C8 inhibitors.
- CYP3A Substrates: Concomitant use may increase the toxicity associated with a CYP3A substrate. Avoid concomitant use of TUKYSA where minimal concentration changes may lead to serious or life-threatening toxicities. If concomitant use is unavoidable, decrease the CYP3A substrate dosage.
- P-gp Substrates: Concomitant use may increase the toxicity associated with a P-gp substrate. Consider reducing the dosage of P-gp substrates where minimal concentration changes may lead to serious or life-threatening toxicity.
Use in Specific Populations
- Lactation: Advise women not to breastfeed while taking TUKYSA and for 1 week after the last dose.
- Renal Impairment: Use of TUKYSA in combination with capecitabine and trastuzumab is not recommended in patients with severe renal impairment (CLcr < 30 mL/min), because capecitabine is contraindicated in patients with severe renal impairment.
- Hepatic Impairment: Reduce the dose of TUKYSA for patients with severe (Child-Pugh C) hepatic impairment.
REF-T1K1161
Indication
TUKYSA is indicated in combination with trastuzumab and capecitabine for treatment of adult patients with advanced unresectable or metastatic HER2-positive breast cancer, including patients with brain metastases, who have received one or more prior anti-HER2-based regimens in the metastatic setting.
Please see full Prescribing Information.
Important Safety Information
Important Safety Information + Indication
Indication
Warnings and Precautions
Warnings and Precautions
-
Diarrhea:
TUKYSA can cause severe diarrhea including dehydration,
hypotension, acute kidney injury, and death. If diarrhea occurs,
administer antidiarrheal treatment as clinically indicated.
Perform diagnostic tests as clinically indicated to exclude other
causes of diarrhea. Based on the severity of the diarrhea,
interrupt dose, then dose reduce or permanently discontinue
TUKYSA.
In HER2CLIMB, when TUKYSA was given in combination with trastuzumab and capecitabine, 81% of patients who received TUKYSA experienced diarrhea, including 0.5% with Grade 4 and 12% with Grade 3. Both patients who developed Grade 4 diarrhea subsequently died, with diarrhea as a contributor to death. Median time to onset of the first episode of diarrhea was 12 days and the median time to resolution was 8 days. Diarrhea led to TUKYSA dose reductions in 6% of patients and TUKYSA discontinuation in 1% of patients. Prophylactic use of antidiarrheal treatment was not required on HER2CLIMB. -
Hepatotoxicity:
TUKYSA can cause severe hepatotoxicity. Monitor ALT, AST, and bilirubin prior to starting TUKYSA, every 3 weeks during treatment, and as clinically indicated. Based on the severity of hepatotoxicity, interrupt dose, then dose reduce or permanently discontinue TUKYSA.
In HER2CLIMB, 8% of patients who received TUKYSA had an ALT increase >5 × ULN, 6% had an AST increase >5 × ULN, and 1.5% had a bilirubin increase >3 × ULN (Grade ≥3). Hepatotoxicity led to TUKYSA dose reductions in 8% of patients and TUKYSA discontinuation in 1.5% of patients.
-
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity:
TUKYSA can cause fetal harm. Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential, and male patients with female partners of reproductive potential, to use effective contraception during TUKYSA treatment and for 1 week after the last dose.
Adverse Reactions
In HER2CLIMB, serious adverse reactions occurred in 26% of
patients who received TUKYSA; the most common (in ≥2% of
patients) were diarrhea (4%), vomiting (2.5%), nausea (2%),
abdominal pain (2%), and seizure (2%). Fatal adverse reactions
occurred in 2% of patients who received TUKYSA including sudden
death, sepsis, dehydration, and cardiogenic shock.
Adverse reactions led to treatment discontinuation in 6% of
patients who received TUKYSA; the most common (in ≥1% of
patients) were hepatotoxicity (1.5%) and diarrhea (1%). Adverse
reactions led to dose reduction in 21% of patients who received
TUKYSA; the most common (in ≥2% of patients) were hepatotoxicity
(8%) and diarrhea (6%).
The most common adverse reactions in patients who received
TUKYSA (≥20%) were diarrhea, palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia,
nausea, hepatotoxicity, vomiting, stomatitis, decreased
appetite, anemia, and rash.
Lab Abnormalities
In HER2CLIMB, Grade ≥3 laboratory abnormalities reported in ≥5% of patients who received TUKYSA were decreased phosphate, increased ALT, decreased potassium, and increased AST.
The mean increase in serum creatinine was 32% within the first 21 days of treatment with TUKYSA. The serum creatinine increases persisted throughout treatment and were reversible upon treatment completion. Consider alternative markers of renal function if persistent elevations in serum creatinine are observed.
Drug Interactions
- Strong CYP3A/Moderate CYP2C8 Inducers: Concomitant use may decrease TUKYSA activity. Avoid concomitant use of TUKYSA.
- Strong or Moderate CYP2C8 Inhibitors: Concomitant use of TUKYSA with a strong CYP2C8 inhibitor may increase the risk of TUKYSA toxicity; avoid concomitant use. Increase monitoring for TUKYSA toxicity with moderate CYP2C8 inhibitors.
- CYP3A Substrates: Concomitant use may increase the toxicity associated with a CYP3A substrate. Avoid concomitant use of TUKYSA where minimal concentration changes may lead to serious or life-threatening toxicities. If concomitant use is unavoidable, decrease the CYP3A substrate dosage.
- P-gp Substrates: Concomitant use may increase the toxicity associated with a P-gp substrate. Consider reducing the dosage of P-gp substrates where minimal concentration changes may lead to serious or life-threatening toxicity.
Use in Specific Populations
- Lactation: Advise women not to breastfeed while taking TUKYSA and for 1 week after the last dose.
- Renal Impairment: Use of TUKYSA in combination with capecitabine and trastuzumab is not recommended in patients with severe renal impairment (CLcr < 30 mL/min), because capecitabine is contraindicated in patients with severe renal impairment.
- Hepatic Impairment: Reduce the dose of TUKYSA for patients with severe (Child-Pugh C) hepatic impairment.
REF-T1K1161
Indication
TUKYSA is indicated in combination with trastuzumab and capecitabine for treatment of adult patients with advanced unresectable or metastatic HER2-positive breast cancer, including patients with brain metastases, who have received one or more prior anti-HER2-based regimens in the metastatic setting.
Please see full Prescribing Information.
TUKYSA is indicated in combination with trastuzumab and capecitabine for treatment of adult patients with advanced unresectable or metastatic HER2-positive breast cancer, including patients with brain metastases, who have received one or more prior anti-HER2-based regimens in the metastatic setting.
Please see full Prescribing Information.
1. Murthy RK, Loi S, Okines A, et al. Tucatinib, trastuzumab, and capecitabine for HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(7):597-609. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1914609 2. TUKYSA. Prescribing information. Seagen Inc.; 2023. 3. Food and Drug Administration. What is a serious adverse event? Updated May 18, 2023. Accessed April 28, 2025. https://www.fda.gov/safety/reporting-serious-problems-fda/what-serious-adverse-event 4. Murthy RK, Loi S, Okines A, et al. Tucatinib, trastuzumab, and capecitabine for HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(7):597-609. Protocol. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1914609 5. Okines A, Paplomata E, Wahl T, et al. Management of adverse events in patients with HER2+ metastatic breast cancer treated with tucatinib, trastuzumab, and capecitabine (HER2CLIMB). Poster presented at: American Society of Clinical Oncology Annual Meeting; May 29-31, 2020. 6. Data on file. Seagen Inc. 7. Curigliano G, Mueller V, Borges V, et al. Tucatinib versus placebo added to trastuzumab and capecitabine for patients with pretreated HER2+ metastatic breast cancer with and without brain metastases (HER2CLIMB): final overall survival analysis. Ann Oncol. 2022;33(3):321-329. doi:10.1016/j.annonc.2021.12.005
